

DOI: https://doi.org/10.46502/issn.1856-7576/2025.19.01.10
Eduweb, 2025, enero-marzo, v.19, n.1. ISSN: 1856-7576
Cómo citar:
Biriukova, D., Chyzhykova, I., Holiak, V., Volkova, M., & Shyshkina, I. (2025). Using online services for the development of listening skills in future foreign language teachers. Revista Eduweb, 19(1), 153-163. https://doi.org/10.46502/issn.1856-7576/2025.19.01.10
Utilización de servicios en línea para el desarrollo de la capacidad de comprensión oral en futuros profesores de lenguas extranjeras
Diana Biriukova
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1721-0122
PhD in Philological Sciences, Associate Professor, University of Customs and Finance, Dnipro, Ukraine.
Inna Chyzhykova
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2722-3258
Senior Lecturer, University of Customs and Finance, Dnipro, Ukraine.
Viktoria Holiak
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3151-9134
Senior Lecturer, University of Customs and Finance, Dnipro, Ukraine.
Maryna Volkova
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1038-7870
PhD in Philological Sciences, Associate Professor, Oles Honchar Dnipro National University, Dnipro, Ukraine.
Iryna Shyshkina
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0027-4020
PhD in Philological Sciences, Associate Professor, Oles Honchar Dnipro National University, Dnipro, Ukraine.
Recibido: 16/01/25
Aceptado: 30/03/25
Abstract
This study examines the effectiveness of online services in developing listening skills and enhancing motivation to learn foreign languages among university students training to become future teachers. Using an experimental and longitudinal design, the research evaluated changes in listening comprehension in control and experimental groups through standardized tests, structured interviews, and the Attitude/Motivation Test Battery (AMTB). Results revealed statistically significant improvements in all listening indicators within the experimental group, as well as increased motivation and reduced anxiety levels. A strong correlation between motivation and listening development was observed. The findings suggest that digital tools such as TED Talks and BBC Learning English can effectively support traditional language instruction, especially when integrated with adaptive pedagogical approaches. Future research should explore long-term impacts and the use of immersive technologies in language education.
Keywords: communicative competence, foreign languages, listening skills, motivation, digital technologies, teacher training.
Resumen
El estudio analiza la efectividad de los servicios en línea en el desarrollo de la comprensión oral y la motivación para aprender lenguas extranjeras en estudiantes universitarios que se preparan como futuros profesores. A través de un diseño experimental y longitudinal, se evaluaron los cambios en las habilidades de escucha de dos grupos (control y experimental) mediante pruebas estandarizadas, entrevistas y el cuestionario Attitude/Motivation Test Battery (AMTB). Los resultados muestran mejoras estadísticamente significativas en el grupo experimental en todos los indicadores de comprensión auditiva, así como un aumento en la motivación y una disminución en los niveles de ansiedad. Se evidenció una alta correlación entre la motivación y el desarrollo de las habilidades de escucha. El estudio concluye que los servicios digitales, como TED Talks o BBC Learning English, pueden ser herramientas eficaces para complementar el aprendizaje tradicional, especialmente si se integran con enfoques pedagógicos adaptativos. Se sugieren investigaciones futuras sobre el impacto a largo plazo y el uso de tecnologías inmersivas.
Palabras clave: competencia comunicativa, lenguas extranjeras, comprensión oral, motivación, tecnologías digitales, formación docente.
Introduction
The relevance of the study is determined by the need to develop effective methods of teaching foreign languages for students of technical majors. The use of interactive online platforms for the development of listening skills is a promising direction. It enables the adaptation of the educational material to the specifics of technical texts and enhances students’ motivation for independent work (Aggarwal, 2023). Research in this area will contribute to the development of new pedagogical technologies that will help to prepare specialists who are able to communicate effectively in an international professional environment.
Listening is an integral part of the comprehensive development of speaking competence (Fayzullayeva, 2023). It is closely related to other types of speech: speaking, reading, and writing. Understanding speech by ear contributes to expanding vocabulary, improving grammatical structures, and forming correct pronunciation. Listening enables immersing oneself in the cultural environment of the language, which is important for the development of intercultural competence (Anggreni et al., 2023).
The task of developing sustainable listening skills is solved by using online services for learning a foreign language. They provide students with unlimited opportunities for developing listening comprehension. A variety of materials, interactive exercises, and the ability to control the pace are just some of the advantages of such platforms. They allow students to get acquainted with different styles of speech. An individual approach, provided by the creation of individual educational trajectories, contributes to effective learning (Frumkina et al., 2020).
The insufficient level of development of listening skills among students is a pressing problem in modern language education and defines the problem of the study. Despite the importance of listening for effective communication in a foreign language, this aspect is often underestimated in curricula. The study focuses on analysing the impact of various teaching methods, in particular online services, on the development of students’ listening skills. Particular attention is paid to the capabilities of interactive and accessible online platforms to stimulate active assimilation of audio materials. The aim of the study is to assess the effectiveness of online services for developing listening and studying students’ motivation to learn a language in students studying to become foreign language teachers.
The aim involves the fulfilment of the following research objectives:
This article proceeds with the following structure. Initially, a comprehensive review of existing literature concerning online services for the enhancement of listening proficiency and the cultivation of motivation in language acquisition is provided. Subsequently, the methodological framework, encompassing the research design, participant sampling, and assessment instruments, is delineated. The ensuing results section presents both quantitative and qualitative findings derived from the study. Following this, a critical discussion of the implications of these results is undertaken. Finally, the conclusion synthesizes the principal insights and proposes avenues for future scholarly inquiry.
Literature Review
In the academic literature, the issue of studying foreign languages in higher education institutions (HEIs) is one of the most relevant in modern linguistic didactics. The study of Dereka (2024) focuses on the issue of the growing international cooperation. According to the researcher, it is determined by the requirements of the labour market and the need to train specialists who have a high level of foreign language proficiency. According to Andrieieva & Kolyaska (2024), language learning in HEIs, involves not only the development of lexical and grammatical knowledge. It should provide for the development of communicative competence, which includes the ability to understand authentic speech, participate in dialogues and create various texts. The researchers place particular emphasis on the importance of integrating modern technologies into the educational process.
A special place in the academic literature is occupied by the problem of developing listening skills as one of the key components of studying a foreign language. In the article by Sam (2024), listening is considered as a process that ensures the perception and understanding of speech by ear. It is the basis for the development of other types of language activities, such as speaking, reading and writing. We share the thesis that listening contributes to the development of lexical, grammatical and communicative skills through contact with authentic language samples.
The importance of authentic material for the development of listening skills should now be emphasized. The article by Chou (2023) emphasizes the role of using audio and video materials that reflect real speech practice. The author examines the impact of technological innovations, such as interactive platforms, mobile applications, and multimedia resources, on the quality of training listening comprehension. The use of innovative digital technologies for the development of listening skills is also covered in the work of Peixoto et al. (2023). The study focuses on how the use of technological innovations takes into account the personal differences of students, their level of language proficiency, and cognitive characteristics. We believe that these works open up new opportunities in the study of the development of listening skills using modern digital technologies.
The work of Tursunovich (2023) emphasizes the role of online services in training listening comprehension, emphasizing their significant potential in the development of students’ speaking competence. Popular online resources used to develop listening skills include such platforms as YouTube, Netflix, BBC Learning English, Duolingo, TED Talks, etc. Researchers note that these resources provide access to authentic language material that covers a wide range of topics and styles of speech. We share the opinion that online services help to familiarize oneself with different accents, speech patterns, and cultural characteristics of native speakers of a particular language.
According to Rashov (2024), the advantages of online services in teaching listening comprehension are their accessibility, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to individual students’ needs. The researcher notes that online tools enable students to learn at their own pace, use subtitles, repeat audio fragments, and adjust the speed of speech. According to Panagiotidis et al. (2023), the interactive features of online services enhance students’ learning motivation. However, researchers also draw attention to the disadvantages of using online services. In particular, students may find it difficult to organize the process of independent learning without proper teacher support. We accept such concerns and consider it appropriate to investigate students’ motivation when using online services in more detail.
According to Badary (2024), the educational capabilities of online services for the development of listening skills depend on their correct use in the educational process. The researcher notes the need to combine online services with traditional teaching methods in order to ensure consistency and control over the assimilation of the material. As Benamara & Benmouhoub (2024) noted, online services can be effective in creating situations of real communication, simulating dialogues, conducting listening comprehension, etc. The researchers state that teachers can use these resources to individualize learning, adapting tasks to the students’ level and their educational needs. We agree with such statements and consider online services to be an excellent educational supplement to the main methods of learning a foreign language.
The use of online services for the development of listening skills is a promising direction in the methodology of learning foreign languages, which requires further research. The issue of personalizing learning taking into account individual cognitive styles and rates of information perception remains poorly studied. An important role is played by motivational factors that affect the effectiveness of self-study, and mechanisms for their support in the online environment. The technological aspect of the problem involves the study of optimal formats of audio materials for the development of listening skills. A promising direction is the creation of immersive learning environments using virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. Psychological aspects that should be studied include the relationship between emotional state and the ability to perceive information audibly during listening.
Methods
Research design
Based on the aim and objectives of the study, it can be defined as experimental and longitudinal, as it studies the change in listening skills over time. It was conducted in several stages. Figure 1 illustrates the research procedure.
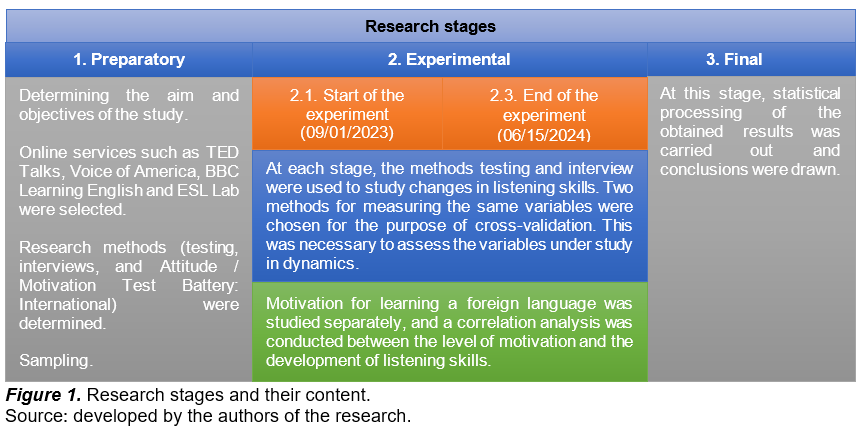
Sampling
The study involved the students of the Department of Foreign Philology, Translation and Professional Language Training at the Faculty of Economics, Business and International Relations of the University of Customs and Finance; and the Department of English Philology at the Faculty of Ukrainian and Foreign Philology and Art History of Oles Honchar Dnipro National University. All students were in their 3rd year at the time of the experiment. The total sample size was 140 people, 70 in the EG, and 70 in the CG. Both groups were homogeneous in terms of foreign language competence. The distribution into groups was made by drawing lots. The inclusion criteria were proficiency in English at level A2, being a full-time student, and permanently residing in Ukraine. The EG students were invited to supplement their studies with materials from platforms such as TED Talks (ESL Brains, n.d.), Voice of America (n.d.), BBC Learning English (n.d.), and ESL Lab (n.d.). These platforms provide authentic audio material for different levels. Access is free of charge. The use of these resources does not violate the principles of academic integrity and copyright and/or other related rights. The study meets the high requirements of academic integrity, ethics, professionalism, and scientific accuracy. The obtained results are interpreted solely for the purpose of obtaining sound data, excluding any discrimination. The respondents provided informed consent to the processing and publication of the obtained results.
Methods
The reliability of the research results was ensured through an assessment of the internal consistency of the instruments and the cross-validation method. A high level of internal consistency indicates that individual elements of the instruments measure the same construct. Cross-validation made it possible to verify that the results obtained are not random and can be generalized to other data samples. The use of these procedures ensured a high level of confidence in the obtained results.
Results
The level of development of listening skills was measured at the beginning, middle, and end of the study using standardized tests and interviews. This made it possible to study the change in skills over time in experimental and control pedagogical conditions. The results of the study of changes in listening skills using standardized tests are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Changes in the level of development of listening skills in the CG and EG at different stages of the study
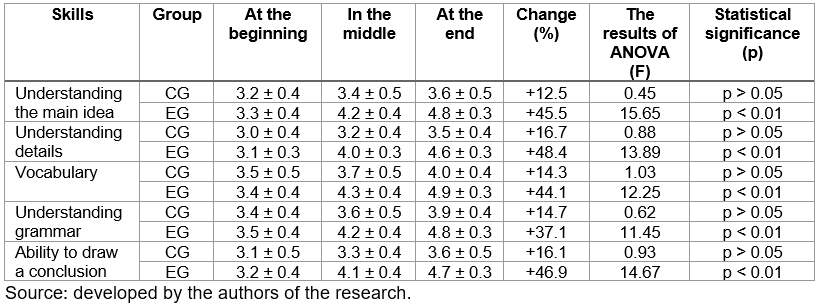
Table 1 demonstrates the initial homogeneity of the CG and EG in all listening parameters, which is confirmed by the close mean values. At the end of the study, the EG showed a statistically significant increase in the results for all indicators, especially in understanding the main idea (+1.6), details (+1.4), and vocabulary (+1.2). This indicates the effectiveness of the training method used. The CG shows smaller changes, which confirms the lack of similar progress without experimental intervention. For the CG, the statistical significance of the ANOVA test showed the absence of significant changes (p > 0.05), which confirms the homogeneity and stability of the results in the group. In the EG, the ANOVA test showed statistically significant changes (p < 0.01) in all aspects of listening, which indicates the effectiveness of the method used. In turn, the results of the interviews using the same criteria demonstrated the results presented in Figure 2.
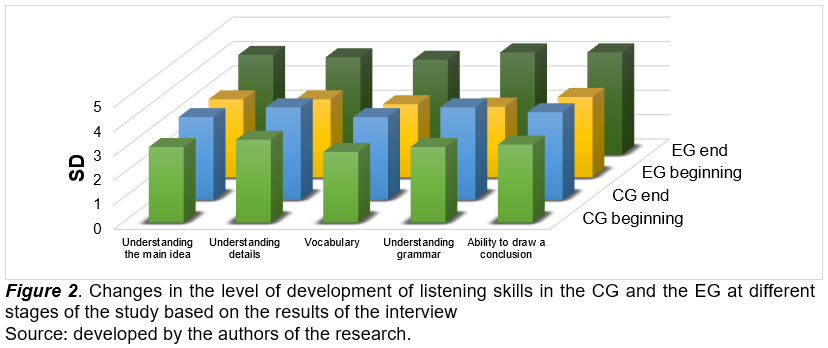
Figure 2 shows that the CG participants significantly improved their results according to all the criteria of the study. The improvement of listening skills in the CG was not so pronounced. On the one hand, this demonstrates the effectiveness of traditional teaching methods. On the other hand, this proves the high efficiency of using online services to develop the auditory perception of a foreign language. The motivation to learn a foreign language was also studied during the experiment. The results are presented in Figure 3.
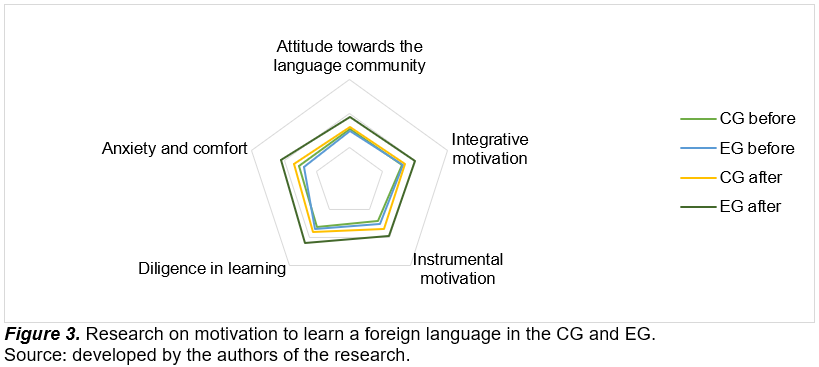
The analysis of the data presented in Figure 3 demonstrates a statistically significant increase in all components of motivation to learn a foreign language in the EG compared to the CG. The most pronounced increase is observed in the indicators of attitude to the language community (Δ = 0.7 points), integrative motivation (Δ = 0.7 points), and diligence in learning (Δ = 0.8 points). At the same time, the level of anxiety in the EG decreased by 1.4 points. These results indicate the high effectiveness of the experimental intervention in enhancing motivation to learn a foreign language. Table 2 shows the correlation between motivation to learn a foreign language and changes in the level of development of listening skills in both groups.
Table 2.
The results of the correlation analysis between motivation to learn a foreign language and changes in the level of development of listening skills in both groups
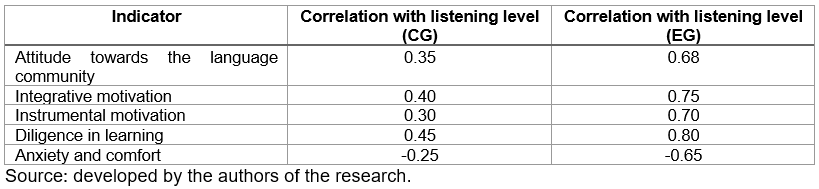
The correlation analysis shows that the EG has a significantly higher level of correlation between positive motivational indicators and the level of development of listening skills compared to the CG. In particular, the correlation coefficient between diligence in learning and the level of listening in the EG is r = 0.80 (p < 0.01). This indicates a strong positive relationship. At the same time, the negative correlation between anxiety and the level of listening in the EG indicates that a decrease in the level of anxiety contributes to an increase in the effectiveness of training listening comprehension.
Discussion
The study revealed significant differences in the relationship between motivational factors and the level of development of listening skills in the EG and CG participants. The EG participants demonstrated significantly stronger positive correlations between attitude to the language community, integrative and instrumental motivation, diligence in learning and the level of development of listening skills. This confirms not only the positive effect of using online services to improve listening skills, but also the ability of these services to positively affect student motivation. At the same time, in the EG, a higher correlation was also observed between the level of anxiety and learning efficiency, which indicates the need to manage the emotional state during learning.
The obtained results indicate the effectiveness of online services in enhancing the positive impact of motivational factors and minimizing the negative impact of anxiety on the success of training listening comprehension. In support of our conclusions, it is worth referring to the results of such works as Bonner et al. (2023) and Ludwig & Tassinari (2023). The researchers provide data to support the effectiveness of online services as additional educational tools in learning a foreign language.
According to Derakhshan & Fathi (2024), online services have become a powerful tool for developing listening skills. The researchers state that they provide access to a wide range of authentic materials that reflect a variety of speech situations. An individualized approach, adaptation to the user’s level, and interactive tools such as subtitles, electronic dictionaries, and feedback contribute to the effective assimilation of the material. Kianinezhad (2023) believes that the use of artificial intelligence technologies allows for the personalization of learning by analysing errors and developing individual improvement strategies. The researcher notes that such high-tech online services allow for continuous improvement of the students’ personal educational trajectory by enhancing their learning motivation. The conclusions presented in both studies confirm the data we obtained on the effectiveness of using online services to improve listening skills.
However, according to Lyu (2024), pure online learning has certain limitations. The lack of direct communication can make it difficult to apply the acquired knowledge in real communicative situations because of the lack of psychological skills to perceive a real speaker. Long work in front of the screen can lead to visual fatigue and reduced concentration. Furthermore, according to Chaiyasat et al. (2024), excessive dependence on technology can negatively affect the development of autonomy in learning.
So, it can be concluded that online services are a valuable addition to traditional methods of teaching listening comprehension. Their effectiveness largely depends on a balanced approach. It involves combining online learning with interactive forms of work that stimulate live dialogue and the development of communicative competencies.
Online services have become a powerful tool for enhancing motivation to learn foreign languages. According to Wei (2022), they owe this to their interactivity, the possibility of personalizing the learning process, and the availability of a wide range of authentic materials. Flexibility in choosing the pace and level of difficulty, gamification, virtual achievements and operational feedback contribute to maintaining a sustainable interest in learning and a sense of progress. According to Negoescu & Mitrulescu (2023), the integration of cultural context through multimedia resources stimulates the development of integrative motivation. The researchers explain this by promoting a deeper understanding of the cultural peculiarities of the language community. The results of our study also prove that the use of online services enhances motivation to learn a foreign language.
However, exclusive reliance on online platforms has certain limitations. Franchisca et al. (2024) draw attention to the fact that the lack of direct interaction with native speakers can negatively affect the development of communication skills. This can reduce the level of emotional involvement in the learning process. According to Rintaningrum (2023), excessive dependence on external stimuli, such as awards or ratings, can lead to the replacement of intrinsic motivation. We agree with the above arguments and insist on the feasibility of further research into the specifics of the formation of motives when learning a foreign language through online services. So, we found that online services are a valuable supplement to traditional methods of learning a foreign language, in particular the development of listening skills. However, their effectiveness depends on a balanced approach that involves a combination of independent work with online platforms and interactive forms of learning. This will help to stimulate lively dialogue and the development of communicative competencies.
The study deepens the theoretical understanding of the impact of online services on the development of listening skills and enhancement of motivation to learn foreign languages. The results confirm the relationship between motivational components and the level of language skills, in particular listening. Practical applications include improving educational programmes, integrating online tools, and creating hybrid learning methods. The results are also useful for platform developers who seek to increase the effectiveness of educational technologies.
Limitations
The results should be interpreted taken into account some limitations. The limited representativeness of the sample (students from only two HEIs) may limit the generalizability of the findings to a wider population. In addition, the methods used to assess listening skills may not fully reflect the complexity of these skills. The limited duration of the experiment does not allow drawing conclusions about the long-term effects of the intervention. Finally, individual differences among participants that were not consistently accounted for may influence the interpretation of the results.
Recommendations
The development of listening skills is a gradual process that requires regular practice. Regular listening to authentic materials, such as podcasts or audiobooks, allows the brain to adapt to different language patterns. Interactive online platforms provide an opportunity to train auditory perception in a playful way, thereby enhancing motivation. Transcript analysis helps to establish connections between the sound of a word and its spelling, contributing to the expansion of vocabulary. Repetition of the listened material consolidates new lexical units and grammatical structures in memory, which ultimately leads to the automation of the process of understanding speech by ear.
Conclusions
The relevance of the obtained results is demonstrating the effectiveness of online learning methods for developing listening skills and enhancing motivation to learn a foreign language. The establishment of a high correlation between motivational indicators and the level of listening in the EG confirms the importance of the targeted use of innovative approaches. The results showed that the level of listening in the EG increased from 3.1 to 4.2 points, in the CG — from 3.2 to 3.4. The correlation between motivational indicators and listening skills in the EG turned out to be high: attitude towards the language community — 0.68, integrative motivation — 0.75, instrumental motivation — 0.70, diligence in learning — 0.80. The negative correlation between anxiety and comfort and the level of listening was –0.65 in the EG. The data confirm the effectiveness of online methods for improving motivation and skills. The obtained data can be used to develop interactive educational programmes that contribute to improving learning outcomes. The results are also interesting for improving pedagogical practices and adapting the educational process to modern digital technologies. The research prospects include studying the long-term impact of online learning on listening and integrating adaptive technologies to personalize the educational process. Furthermore, it is important to analyse the effectiveness of the methods that combine online services with traditional approaches.
Bibliographic references
Aggarwal, D. (2023). Integration of innovative technological developments and AI with education for an adaptive learning pedagogy. China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology, 23(2), 709-714. Retrieved from http://surl.li/idxndt
Andrieieva, M., & Kolyaska, Y. (2024). The features of mastering foreign language vocabulary by students of non-language higher education institutions. Youth & Market, 10(230), 160-164. https://doi.org/10.24919/2308-4634.2024.314387
Anggreni, K., Sinambela, E., & Manurung, W. M. (2023). Improving the vocabulary mastery and listening skill at junior high school using Taylor Swifts songs. IDEAS: Journal on English Language Teaching and Learning, Linguistics and Literature, 11(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.24256/ideas.v11i1.3798
Badary, E. M. M. (2024). Impact de l’usage du micro-apprentissage sur le développement des compétences de la compréhension orale et de la motivation chez les futurs enseignants de FLE. Sohag University International Journal of Educational Research, 9(9), 397-489. https://doi.org/10.21608/suijer.2024.339404
BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Podcasts. BBC. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/english/podcasts
Benamara, F. C. E., & Benmouhoub, F. (2024). The role of the French-language press in improving oral expression (Doctoral dissertation), Ibn Khaldoun-Tiaret University. Retrieved from http://dspace.univ-tiaret.dz:80/handle/123456789/14902
Bonner, E., Lege, R., & Frazier, E. (2023). Large language model-based artificial intelligence in the language classroom: practical ideas for teaching. Teaching English with Technology, 23(1), 23-41. Retrieved from https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1167809
British Council. (n.d.). Understand your English level. LearnEnglish. Retrieved from https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/english-levels/online-english-level-test
Chaiyasat, C., Srimalee, P., Wetprasit, A., & Williamson, P. (2024). An explanatory sequential mixed-methods study of Thai English as a foreign language students’ engagement with emergency online learning in an English medium instruction university. E-Learning and Digital Media. https://doi.org/10.1177/20427530241239423
Chou, M.-H. (2023). Strategies for interactive listening in modern foreign language learning. Language awareness, 32(1), 169-191. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658416.2022.2047194
Derakhshan, A., & Fathi, J. (2024). Grit and foreign language enjoyment as predictors of EFL learners’ online engagement: The mediating role of online learning self-efficacy. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 33(4), 759-769. Retrieved from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40299-023-00745-x
Dereka, K. (2024). Formation of foreign-language communicative competencies of students of professional pre-higher education institutions. Scientific Journal of Polonia University, 65(4), 19-25. https://doi.org/10.23856/6502
ESL Brains. (n.d.). Lesson topic: TED Talks. Retrieved from https://eslbrains.com/lesson_topic/ted-talks/
ESL Lab. (n.d.). Academic English. ESL Lab. Retrieved from https://www.esl-lab.com/academic-english/
Fayzullayeva, N. (2023). The improving of listening skill. Modern Science and Research, 2(10), 272-276. Retrieved from https://inlibrary.uz/index.php/science-research/article/view/25086
Franchisca, S., Sari, M. N., Nurfitri, N., Nelloe, M. K., Mulyapradana, A., & Fitriani, N. (2024). The Impact of Motivation on Foreign Language Learning: A Longitudinal Study. Journal on Education, 6(2), 11082-11093. Retrieved from: https://www.jonedu.org/index.php/joe/article/view/4911
Frumkina, A., Diachenko, M., Polyezhayev, Y., Savina, N., & Hadi, F. (2020). Readiness of future teachers for integrated teaching of educational subjects in foreign language. Práxis Educacional, 16(38), 502-514. https://doi.org/10.22481/praxisedu.v16i38.6023
Gardner, R. C. (2004). Attitude/Motivation Test Battery: International AMTB Research Project. Canada: The University of Western Ontario. Retrieved from https://publish.uwo.ca/~gardner/docs/englishamtb.pdf
Kianinezhad, N. (2023). Effective methods of teaching foreign languages online: A global view. TESOL and Technology Studies, 4(1), 45-59. https://doi.org/10.48185/tts.v4i1.846
Ludwig, C., & Tassinari, M. G. (2023). Foreign language learner autonomy in online learning environments: the teachers’ perspectives. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching, 17(2), 217-234. https://doi.org/10.1080/17501229.2021.2012476
Lyu, B. (2024). The effect of self-regulated learning and community of inquiry on the online learning engagement of Chinese as foreign language learners. Education Sciences, 14(7), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14070691
Negoescu, A. G., & Mitrulescu, C. M. (2023). Using technology to increase students’ motivation for learning a foreign language. International Conference Knowledge-Based Organization, 29(2), 210-214. Retrieved from https://intapi.sciendo.com/pdf/10.2478/kbo-2023-0059
Panagiotidis, P., Krystalli, P., & Arvanitis, P. (2023). Technology as a motivational factor in foreign language learning. European Journal of Education (EJED), 6(1), 69-84. https://doi.org/10.26417/ejed.v1i3.p43-52
Peixoto, B., Bessa, L. C. P., Gonçalves, G., Bessa, M., & Melo, M. (2023). Teaching EFL with immersive virtual reality technologies: A comparison with the conventional listening method. IEEE Access, 11, 21498-21507. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3249578
Rashov, O. (2024). Modern methods of teaching foreign languages. International Scientific and Current Research Conferences, 1(1), 158-164. Retrieved from https://orientalpublication.com/index.php/iscrc/article/view/1684
Rintaningrum, R. (2023). Technology integration in English language teaching and learning: Benefits and challenges. Cogent Education, 10(1), 2164690. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2022.2164690
Sam, R. (2024). Factors causes students low English language learning: A case study in the National University of Laos. International Journal of English Language Education, 1(1). https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4850858
Tursunovich, R. I. (2023). Development of communicative competence in teaching foreign language for professional purposes. Proceedings of International Conference on Scientific Research in Natural and Social Sciences, 2(1), 26-33. Retrieved from https://econferenceseries.com/index.php/srnss/article/view/759
Voice of America. (n.d.). Learning English. Retrieved from https://learningenglish.voanews.com
Wei, Y. (2022). Toward technology-based education and English as a foreign language motivation: A review of literature. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 870540. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.870540

Este artículo está bajo la licencia Creative Commons Atribución 4.0 Internacional (CC BY 4.0). Se permite la reproducción, distribución y comunicación pública de la obra, así como la creación de obras derivadas, siempre que se cite la fuente original.